17 Which of the Following Is the Primary Hypoglycemic Hormone
And halogens C alkali metals and halogens D noble gases and alkali metals. In the postabsorptive state most cells use _______ for energy.
10 marks b Describe the mechanism of action for each of the drugs mentioned above.

. Adrenal glands to release cortisol. Stimulate certain endocrine glands to secrete hormones. Progesterone is a progestational hormone.
Reported attenuated glucagon growth hormone and cortisol responses but no change in epinephrine response and increased norepinephrine release during subcutaneous insulin-induced hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes who had no clinical evidence of autonomic neuropathy. A halogens and noble gase B alkaline earth metals. Pituitary gland to release growth hormone.
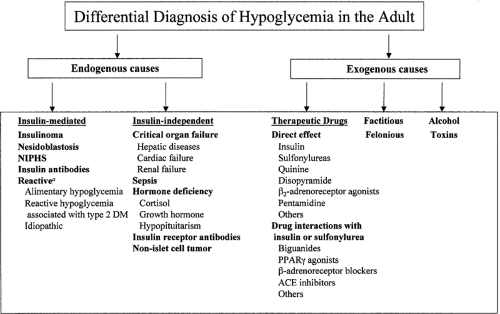
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS 40 MARKS Answer ALL questions 1. Hypoglycemia also called low blood sugar is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal typically below 70 mgdL. Severe hypoglycemia is often the primary barrier to achieving glycemic targets in people with type 1 diabetes and occurs frequently during sleep or in the presence of hypoglycemia unawareness.
A mutation occurs in the sequence leading to. 3The growth hormone is responsible for rapid growth. Whipples triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes.
The sympathoadrenal response to hypoglycemia is reduced during sleep and following exercise or alcohol consumption 2627. Page 6 of 6 SECTION III. Antidiuretic hormone ADH The hormone that antagonizes the effects of glucagon by supressing the breakdown of glycogen is_____________.
2The luteinizing hormone controls the release of the ovum for fertilization. 85 From NCERT. All of these hormones cause the liver to release glucose into the blood but sometimes these hormones do not raise the blood glucose level enough to overcome the hypoglycemia.
D A and C. Which cell type within the pancreatic islets secretes the hormone insulin. It increases the flow of blood to adrenal cortex and also increases the concentration of cholesterol and steroids.
E all of the above. A sneaky diabetic tried to lower her glucose by working out and watching her diet 1 or 2 days before her appointment. Hence out of all given hormones insulin is hypoglycemic because it lowers the level of sugar in blood.
Glucagon Hypoglycemic hormone Answer. Complete the chart showing hormone and hormonal diseases MARCH-2014. 83 Other studies have reported reduced glucagon but.
Glucagon which is stimulated by low plasma glucose levels increases hepatic glucose production primarily by stimulating glycogenolysis. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mgdL symptoms associated with hypoglycemia and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. C Ketones are produced during fatty acid metabolism.
This result in increased output of steroid hormone cortisol from adrenal cortex. These deficiencies are uncommon in patients without type 1 or advanced type 2 diabetes and usually present with additional signs andor symptoms 1. Deficiencies in counter-regulatory hormones cortisol glucagon and epinephrine may result in hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia may result in. Identify the sequences where the mutation. Which of the following is the primary hypoglycemic hormone.
The hormone that increases water retention by the kidneys reduces urine volume and helps prevent dehydration is _____. Pancreas to release glucagon. Glucagon works antagonist of insulin.
For instance Bolli et al. A Describe five adverse effects associated with use of antipsychotic drugs. Which cellular component of the thyroid synthesizes and secretes thyroid hormone T3 and T4.
A Classify the drugs used in treatment of heart failure naming two examples in each case. Hyperglycemic hormone is glucagon while hypoglycemic hormone is insulin. Classify the following as characteristics of the endocrine system.
A Gluconeogenesis occurs during the absorptive state. Which of the following is responsible for hyperglycemia. This sequence encodes for a particular protein that helps bacteria move.
C Ketones are produced during fatty acid metabolism. Kicks in when you have hypoglycemia A glycosylated hemoglobin. 4Pubic hair growth occurs with the release of hormones from the hypothalamus.
Luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormones are examples of gonadotrophic hormone. A testosterone B cortisol C insulin D melatonin. 27The primary stimulus for the release of cortisol is A nerve stimulation from hypothalamus B ACTH C increased blood glucose levels D increased levels of sodium in the blood.
- Communicates by means of hormones - Reacts more slowly to stimuli - May continue responding long after stimulus stops - Adapts relatively slowly. Epinephrine increases glucose production directly by mobilizing the gluconeogenic precursors such as alanine and lactate from muscle and glycerol from fat. Select ALL the correct answers.
Website not working properly. So glucagon is considered as hyperglycemic hormone. Parathyroid hormone PTH is hypercalcemic hormone.
1The luteinizing hormone works during the luteal phase of ovulation and does not have an influence on primary sexual organ growth. So the correct answer is Insulin. Insulin is the major actor in causing hypoglycemia.
B Most of the glycogen stores of the body are found here. The rest of the time she spent the day in front of the television and eating chocolates. 4 All of the above.
Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar is a condition that occurs when level of blood sugar decreases to below normal level. Which of the following is the primary effect of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4. There are many other hormones that modulate the release of insulin.
Promote heat-generating metabolic reactions.

Q 145 180 Which Of The Following Is Not The Correct Match Between The Characteristic Listed And Example Quoted O Hyperglycemic Hormone Cortisol Hypoglycemic Hormone Glucagon Hypocalcemic Hormone Thyrocalcitonin O

Q 145 180 Which Of The Following Is Not The Correct Match Between The Characteristic Listed And Example Quoted O Hyperglycemic Hormone Cortisol Hypoglycemic Hormone Glucagon Hypocalcemic Hormone Thyrocalcitonin O
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationthe Adult Hypoglycemic Patient Tips For Emergency Department Management Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
No comments for "17 Which of the Following Is the Primary Hypoglycemic Hormone"
Post a Comment